Excellent Capacity Dressing For Use On Moderately To Heavily Exuding Wounds.
MD DME Silicone Foam Dressing consists of a gentle silicone wound contact layer, a super
absorbent pad layer, and a vapor-permeable and waterproof film. It is an ideal dressing for
advanced wound exudate management. The multi-layer construction facilitates dynamic
fluid management to provide an optimal moist wound environment, which promotes wound
healing, minimizes trauma, and can reduce pain during dressing changes.
What Is The Collagen?
Collagen is the unique, triple helix protein molecule, which forms the major part of the extracellular dermal matrix LECML together with the
glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, leminin, fibronectin, elastin and cellular components. Collagen, the most abundant protein in animal sus
accounts for 80%-90% of the dry weight of the dermis. Mainly produced by feroblasts, at least 29 genetically distinct collagers have currently
been identified with six of these being present In the skin. Colagen type i comprises approximately 90% of collagen in the skin. Type 1 and lll are
important for wound healing.
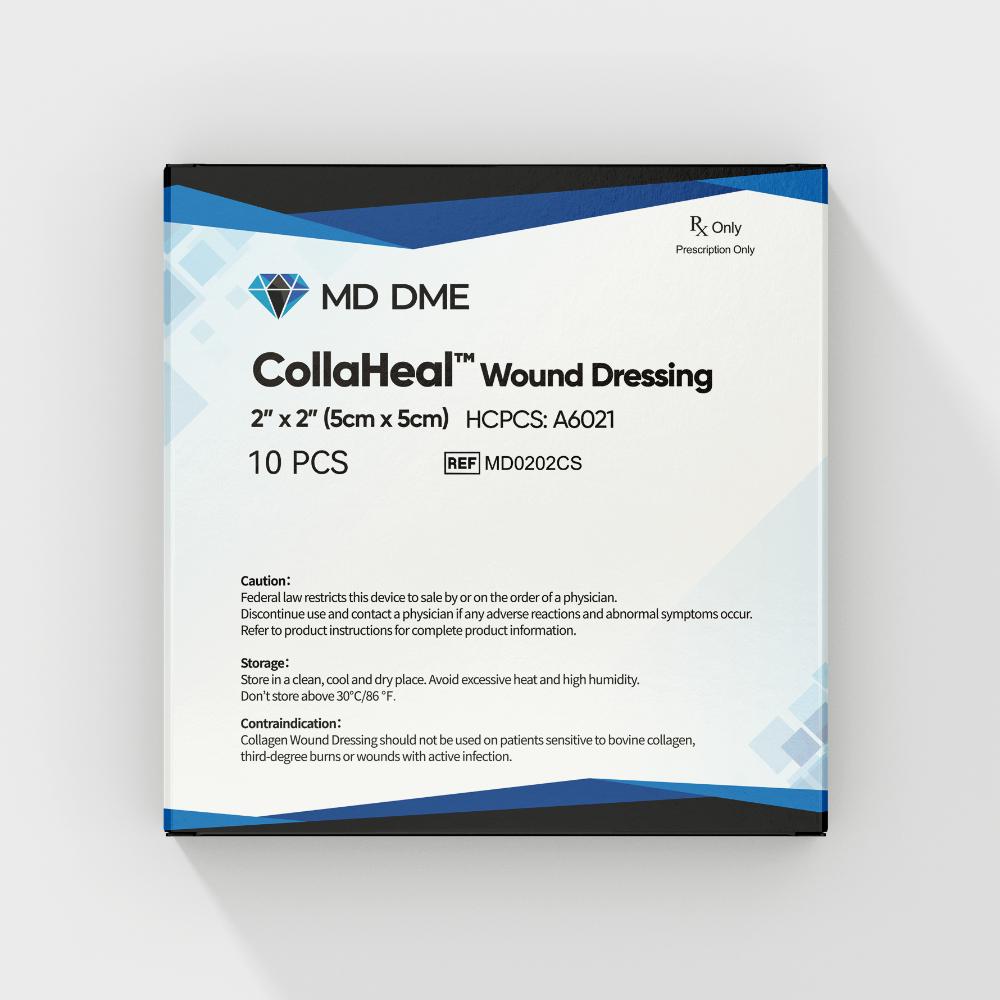
Advantages About MD DME Collaheal™
The dressing, which falls under the category of a permanent contact device, is
non-pyrogenic, super conformant, entirely absorbable, and simple to use
It serves as a porous scaffold for cell proliferation and migration and may be
used as hemostatic dressing for surface wounds.
Dressings are suitable for use under compression with proper supervision by a
healthcare professional
The product's strength and enzyme resistance are increased without the use of
chemical additives and with the aid of sale cross-linking technology
Excellent technical level and integrity of results
Collagen Dressings In Wound Management
MD DME Silicone Foam Dressing consists of a gentle silicone wound contact layer, a super
absorbent pad layer, and a vapor-permeable and waterproof film. It is an ideal dressing for
advanced wound exudate management. The multi-layer construction facilitates dynamic
fluid management to provide an optimal moist wound environment, which promotes wound
healing, minimizes trauma, and can reduce pain during dressing changes.
Product Overview
100% Type I collagen of bovine, no fillers.
Original triple helix structure makes it have good biocompatibility.
Strong absorption capacity, can absorb 38 times of its own weight.
Cover the wound to form a physical barrier and protect the wound from external environment.
Gel after absorption and maintains a wet environment conducive to wound healing.
Sufficient mechanical strength for easy application.

High-Performance Collagen Wound Dressing
- Collagen Wound Dressing offers a greater collagen content than comparable products since it is composed 100% type I bovine collagen.
- Collagen Wound Dressing has high biocompatibility, and the cells bridged on the dressing have a superior growth trend, according to the findings of cell proliferation tests for the 1st, 4th and 7th days.
- Collagen Wound Dressing has good mechanical strength, which provides easy application for medical professional.
- Collagen Wound Dressing softly treats the wound bed and wound edge because it is mildly acidic, which is closer to the pH value of skin.
- Collagen Wound Dressing has strong weight capacity of absorption. It has a significant capacity for absorption, which is helpful in preserving the moist environment for wound healing and reduces the danger of maceration.
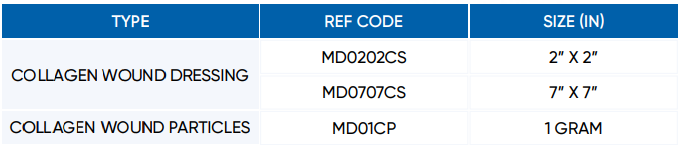
Product Specifications
MD DME Collagen Wound Dressing has an excellent and homogeneous fiber network structure,
which provides high biocompatibility and aids in wound healing, as is seen in the electron
microscope image.
Contraindications
Patients who are sensitive to bovine collagen, those with
third-degree burns, or wounds that show active signs of
infection should not use collagen wound dressings.
Indications
MD DME Collagen Wound Dressing is intended for the management of wounds including:
- Full thickness and partial thickness wounds
- Pressure ulcers
- Venous ulcers
- Ulcers caused by mixed vascular etiologies
- Diabetic ulcers
- Partial thickness burns
- Donor sites and other bleeding surface wounds
Abrasions - Traumatic wounds healing by secondary intention
Dehisced surgical incisions